What’s the state of the global economy right now? Is the economy slowing in 2022? The simple answer is yes, but the global economy’s problem is more complicated than that.
What’s the state of the global economy in 2022?
The global outlook has deteriorated dramatically in 2022 due to growing prices, vigorous monetary tightening, and uncertainty from the Ukraine conflict and continuing pandemic.
Rising food and energy costs are eroding actual earnings and causing a worldwide cost-of-living crisis, particularly for the most vulnerable.
The world’s three major economies, the United States, China, and the European Union, are all slowing, with severe consequences for other nations.
Rising government borrowing rates and massive capital outflows are posing new fiscal and balance-of-payments concerns for many developing countries. Looking at the projections below, we can clearly see that the global economy is slowing, and a recession might be something that will happen in the future years.
IMF growth projections: 2022
Let’s take a closer look to the latest growth projections that the International Monetary Fund made in their latest update.
| Country | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
| United States | 5.7% | 2.3% | 1.0% |
| Euro Area | 5.4% | 2.6% | 1.2% |
| China | 8.1% | 3.3% | 4.6% |
| Germany | 2.9% | 1.2% | 0.8% |
| France | 6.8% | 2.3% | 1.0% |
| Italy | 6.6% | 3.0% | 0.7% |
| Spain | 5.1% | 4.0% | 2.0% |
| Japan | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.7% |
| United Kingdom | 7.4% | 3.2% | 0.5% |
| Canada | 4.5% | 3.4% | 1.8% |
| Russia | 4.7% | -6.0% | -3.5% |
| Mexico | 4.8% | 2.4% | 1.2% |
| Brazil | 4.6% | 1.7% | 1.1% |
| Saudi Arabia | 3.2% | 7.6% | 3.7% |
| Nigeria | 3.6% | 3.4% | 3.2% |
Source : IMF Projections
The IMF informed that growth is forecast to fall from 6.1 percent last year to 3.2 percent in 2022, a 0.4 percentage point lower than predicted in the World Economic Outlook for April 2022.
Lower growth earlier this year, lower consumer spending power, and tighter monetary policy have all led to a 1.4 percentage point negative correction in the US. Further tightening and a worsening real estate crisis in China slowed growth by 1.1 percentage point, with huge global ramifications. Europe has seen significant downgrades due to the Ukraine conflict and stricter monetary policy.
Because of rising food and energy prices and persistent supply-demand imbalances, global inflation is expected to reach 6.6 percent in advanced economies this year and 9.5 percent in emerging and developing economies, representing a 0.9 and 0.8 percentage point increase, respectively.
In 2023, when global output is predicted to expand by just 2.9 percent, disinflationary monetary policy is expected to take effect.
Inflation is the most significant challenge the world faces
Let us first define inflation as an increase in the prices of goods and services over time. Economists use a price index to calculate inflation to assess price fluctuations in various commodities and services.
While various indexes exist, the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI -U) is one of the most extensively used. It analyzes price changes in a hypothetical basket of products and services for urban consumers, such as food, clothes, and automobiles.
Why is inflation high in 2022?
The high inflation rate has various causes, many of which are connected to the Covid 19 outbreak.
The high inflation rate has three significant factors:
– increased household demand and supply chain restrictions induced by the pandemic;
– the Ukraine situation;
– the presence of a strong labor market.
At the start of the pandemic, customers spent less due to lockdowns and began saving more. When the Covid 19 spending limitations were annulled, people began spending more. On the other hand, businesses were unable to satisfy the rise in consumer demand since many had reduced output due to the outbreak, resulting in supply delays and labor and essential component shortages.
A Pew Research Center analysis of data from 44 advanced economies finds that nearly all consumer prices have risen substantially since pre-pandemic times.
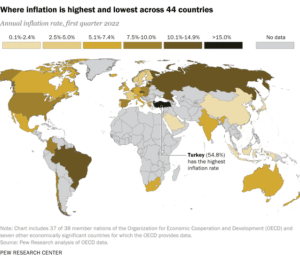
Image rights: Pew Research Center
In 37 of these 44 nations, average annual inflation was at least twice as high in the first quarter of this year as in the first quarter of 2020, when COVID -19 was starting. In 16 nations, inflation was more than four times greater than a year ago in the first quarter.
Turkey had the highest inflation rate among the surveyed countries in the first quarter of 2022: 54.8%. Turkey has had high inflation for years, but it accelerated in late 2021 when the government adopted unconventional economic strategies, such as lowering interest rates instead of raising them.
Whatever the absolute level of inflation in each country, most followed the same basic pattern: relatively low levels before the COVID -19 pandemic in the first quarter of 2020; stagnant or falling rates for the rest of the year and into 2021, when many governments severely curtailed most economic activity; and rising rates from mid-to-late 2021, as the world struggled to return to something resembling normalcy.
Inflation in the USA, is the US economy slowing in 2022?

In the first quarter of this year, the annual inflation rate in the United States was slightly under 8.0%, placing 13th out of 44 nations evaluated. The first-quarter inflation rate in the United States was more than four times greater than the first-quarter inflation rate in 2020.
Inflation looked like a minor concern two years ago, when millions of Americans were unemployed and central bankers and politicians were attempting to pull the United States economy out of a pandemic-induced recession. Many of the same authorities maintained a year later, when unemployment was lower and inflation was higher, that the price increase was “temporary,” the consequence of congested supply chains, labor shortages, and other issues that would be resolved sooner than later.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics most recent report, annual inflation was 8.6% in May, the highest level since 1981, as assessed by the Consumer Price Index. Other inflation measures have grown dramatically in the last year, although not at the same rate as the CPI.
For entire generations of Americans, significant price rises appeared to be a thing of the past since inflation in the United States had been so low for so long. Annual inflation averaged roughly 2.3% per month between 1991 and 2019, exceeding 5.0% only four times.
Is China’s economy slowing down in 2022?
In 2022, the Chinese economy is expected to slow. After a promising start in early 2022, China’s economic normalization has been disrupted by the largest COVID -19 wave in two years. The World Bank predicts 4.3 percent real GDP growth in 2022, a 0.8 percentage point decrease from the December China Economic Update. This negative revision mostly reflects the economic harm caused by Omicron outbreaks and protracted shutdowns in portions of China from March to May.
World Economic Outlook 2023 – What does the World Bank predict for 2023?
East Asia and Pacific: Growth is expected to slow to 5.1% in 2022 before improving marginally to 5.2% in 2023.
Growth in Europe and Central Asia is expected to slow to 3.0% in 2022 and 2.9% in 2023.
Growth in Latin America and the Caribbean is projected to decline to 2.6% in 2022 before picking up slightly to 2.7% in 2023.
Growth in the Middle East and North Africa is expected to increase to 4.4% in 2022 before declining to 3.4% in 2023.
South Asia: growth will increase to 7.6% in 2022 before declining to 6.0% in 2023.
More information can be found in this press release by the World Bank.
Conclusion
As increasing prices continue to erode global living standards, governments should prioritize inflation management. Tighter monetary policy will, without question, have significant economic effects, but postponing them would only worsen them.
Targeted fiscal assistance can help mitigate the impact on the most vulnerable. Still, with government finances already stretched due to the epidemic and the need for anti-inflationary general macroeconomic policies, such initiatives must be offset by higher taxes or reduced government spending.
Tightening monetary conditions will also impact financial stability, necessitating the wise use of macroprudential instruments and changes to the debt control framework.
Measures to mitigate the specific impact on energy and food costs should target the most vulnerable people while avoiding pricing distortions.
The pandemic also influenced the workplace as employees ever knew it, resulting in people losing loyalty towards the company when they stopped their work-from-home policies and were recalled to work – physically. The slowing of the economy can be indirectly influenced by many employees losing morale and deciding to quiet quit.
Will there be a recession? Will the global economy increase? There are a lot of factors to be taken into consideration, but without good economic policies, there is a possibility of a global recession. An economic forecast for the next 5 years, or even for the next 2-3 years, is, at the moment – very hard to project.
Your success story begins with our tailored solutions!
Our team specializes in crafting tailored solutions to meet your unique challenges and goals, providing you with the expertise you need to succeed.